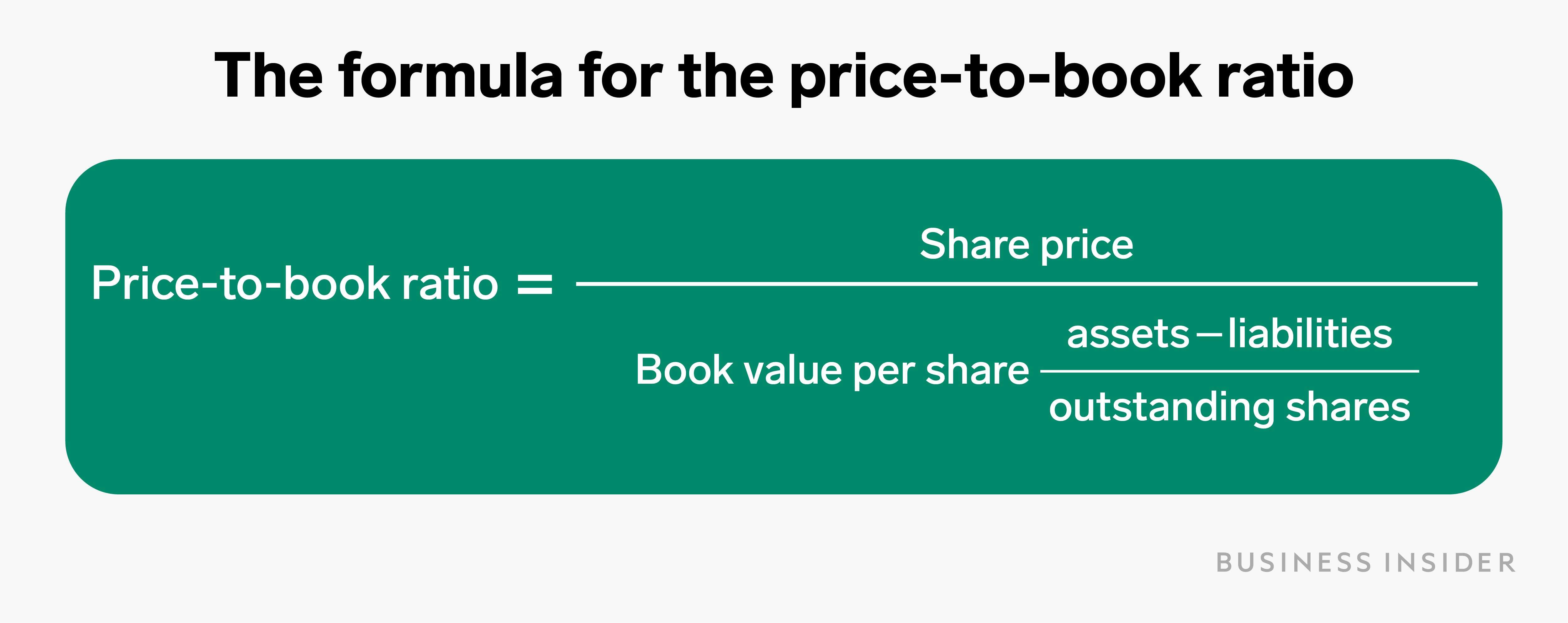
Yes, if a company’s liabilities exceed its assets, the BVPS can be negative, signaling potential financial distress. By multiplying the diluted share count of 1.4bn by the corresponding share price for the year, we can calculate the market capitalization for each year. The book value of equity (BVE) is the value of a company’s assets, as if all its assets were hypothetically liquidated to pay off its liabilities.
Online Investments
The market value per share is a company’s current stock price, and it reflects a value that market participants are willing to pay for its common share. The book value per share is calculated using historical costs, but the market value per share is a forward-looking metric that takes into account a company’s earning power in the future. With increases in a company’s estimated profitability, expected growth, and safety of its business, the market value per share grows higher. Significant differences between the book value per share and the market value per share arise due to the ways in which accounting principles classify certain transactions.
- Alternatively, Book Value can be calculated as the total of the overall Shareholder Equity of the company.
- There is a difference between outstanding and issued shares, but some companies might refer to outstanding common shares as issued shares in their reports.
- It’s important to use the average number of outstanding shares in this calculation.
- SoFi doesn’t charge commissions, but other fees apply (full fee disclosure here).
- Value investors look for relatively low book values (using metrics like P/B ratio or BVPS) but otherwise strong fundamentals in their quest to find undervalued companies.
Free Financial Modeling Lessons
The number is clearly stated as a subtotal in the equity section of the balance sheet. To calculate BVPS, you need to find the number of shares outstanding, which is also usually stated parenthetically next to the common stock label (on Yahoo! Finance, it’s located in Key Statistics). What we’re looking for is the number of shares outstanding, not simply issued. The two numbers can be different, usually because the issuer has been buying back its own stock.
Book Value Per Share vs. Market Stock Price: What is the Difference?
SoFi doesn’t charge commissions, but other fees apply (full fee disclosure here). Knowing what book value per share is, how to calculate it, and how it differs from other calculations, can add yet another tool to an investor’s tool chest. This means that each share of the company would be worth $8 if the company got liquidated. Now, let’s say that you’re considering investing in either Company A or Company B. Given that Company B has a higher book value per share, you might find it tempting to invest in that company. However, you would need to do some more research before making a final decision.
How to Increase Book Value Per Share
If the company’s BVPS increases, investors may consider the stock more valuable, and the stock’s price may increase. On the other hand, a declining book value per share could indicate that the stock’s price may decline, and some investors might consider that a signal to sell the stock. It can and should be used as a supplement to other valuation approaches such as the PE approach or discounted cash flow approaches. Like other multiple-based approaches, the trend in price/BVPS can be assessed over time or compared to multiples of similar companies to assess relative value. If a company has a book value per share that’s higher than its market value per share, it’s an undervalued stock.

In contrast, video game companies, fashion designers, or trading firms may have little or no book value because they are only as good as the people who work there. Book value is not very useful in the latter case, but for companies with solid assets, it’s often the No.1 figure for investors. By repurchasing 1,000,000 common shares from the company’s shareholders, the BVPS increased from $3.00 to $4.50. An investor can apply BVPS to a stock by analyzing the company’s balance sheet. Specifically, an investor will need total asset value, cost of acquiring an asset, and accumulated depreciation of corporate assets which helps provide the most accurate BVPS figure. An even better approach is to assess a company’s tangible book value per share (TBVPS).
As noted above, another way to calculate book value is to subtract a business’ total liabilities from its total assets. Another way to increase BVPS is for a company to repurchase common stock from shareholders. Assume XYZ repurchases 200,000 shares of stock, and 800,000 shares remain outstanding. The company generates $500,000 in earnings and uses $200,000 of the profits to buy assets, its common equity increases along with BVPS. If XYZ uses $300,000 of its earnings to reduce liabilities, common equity also increases.
It can be defined as the net asset value of the firm or company that can be calculated as total assets, less intangible assets (goodwill, patents, etc.), and liabilities. Further, Book Value Per Share (BVPS) can be computed based on the equity of the common shareholders in the company. While corporate debt holders and preferred shareholders are entitled to a fixed series of cash payments, the cash flow in excess of those amounts is essentially the property of the common shareholders. The value of a common stock, therefore, is related to the monetary value of the common shareholders’ residual claim on the corporation – the net asset value or common equity of the corporation. It may not include intangible assets such as patents, intellectual property, brand value, and goodwill. It also may not fully account for workers’ skills, human capital, and future profits and growth.
BVPS is what shareholders receive if the firm is liquidated, all tangible assets are sold, and all liabilities are paid. The book value per share (BVPS) ratio compares the equity held by common stockholders to the total number of outstanding shares. To put it simply, this calculates a company’s per-share total assets less total liabilities. superstream improves the australian superannuation system Book value per common share (or, simply book value per share – BVPS) is a method to calculate the per-share book value of a company based on common shareholders’ equity in the company. The book value of a company is the difference between that company’s total assets and total liabilities, and not its share price in the market.
There is also a book value used by accountants to value the assets owned by a company. This differs from the book value for investors because it is only used internally for managerial accounting purposes. Comparing BVPS to the market price of a stock is known as the market-to-book ratio, or the price-to-book ratio. That said, looking deeper into book value will give you a better understanding of the company. In some cases, a company will use excess earnings to update equipment rather than pay out dividends or expand operations.
In theory, book value should include everything down to the pencils and staples used by employees, but for simplicity’s sake, companies generally only include large assets that are easily quantified. The formula states that the numerator part is what the firm receives by the issuance of common equity. That figure increases or decreases depending upon whether the company is making a profit or loss, and then finally, it decreases by issuing dividends and preference stock.





